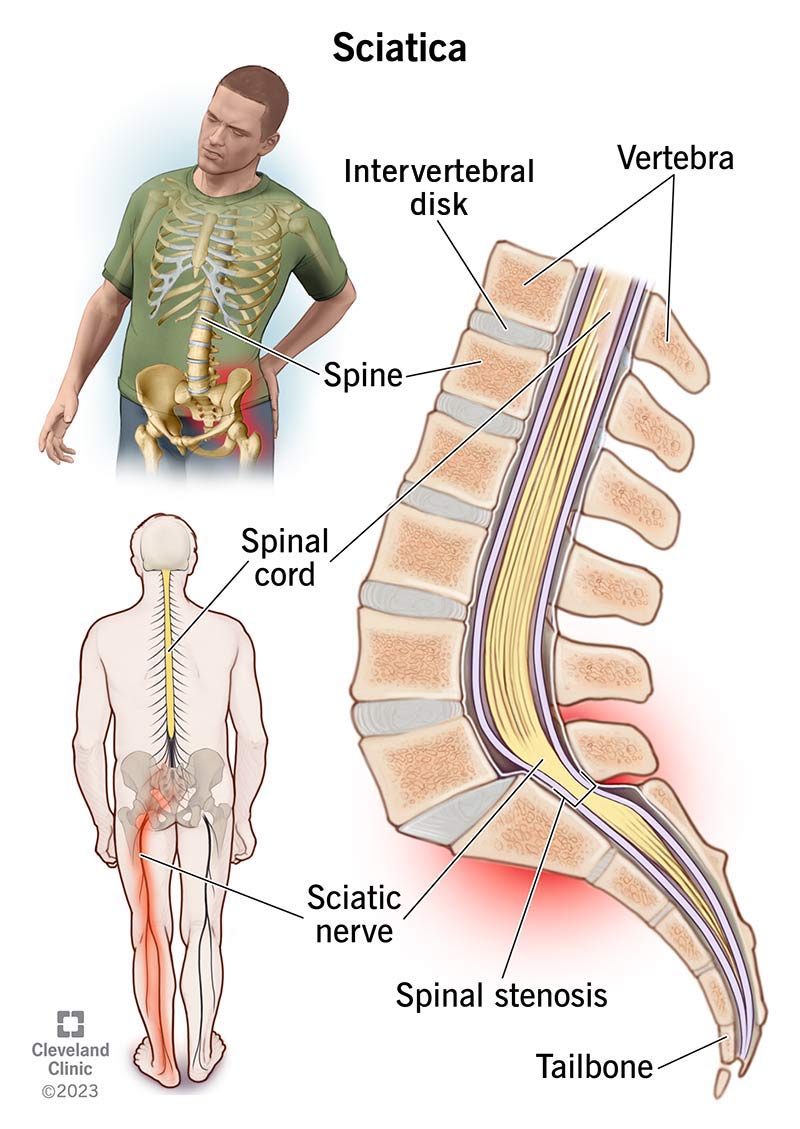
Are you tired of living with low back pain? You’re not alone. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, lower back pain affects over 80% of adults at some point in their lives. It’s a common complaint that can make even the simplest tasks feel like climbing a mountain.
Will Anti-Seizure Meds Ease Low Back Pain?
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of anti-seizure medications and explore whether they can really help ease low back pain. But first, let’s set the stage:
The Connection Between Neurological Disorders and Low Back Pain
While it may seem unrelated at first glance, research has shown that there is a significant link between neurological disorders like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease, and chronic low back pain. In fact, studies have found that people with neurological conditions are more likely to experience low back pain than the general population. This raises an important question: can medications designed to treat seizures and other neurological conditions also help alleviate low back pain?
In this section, we’ll explore the science behind anti-seizure medications and how they might be used to treat low back pain. We’ll examine the mechanisms by which these medications work, as well as their potential benefits and drawbacks.
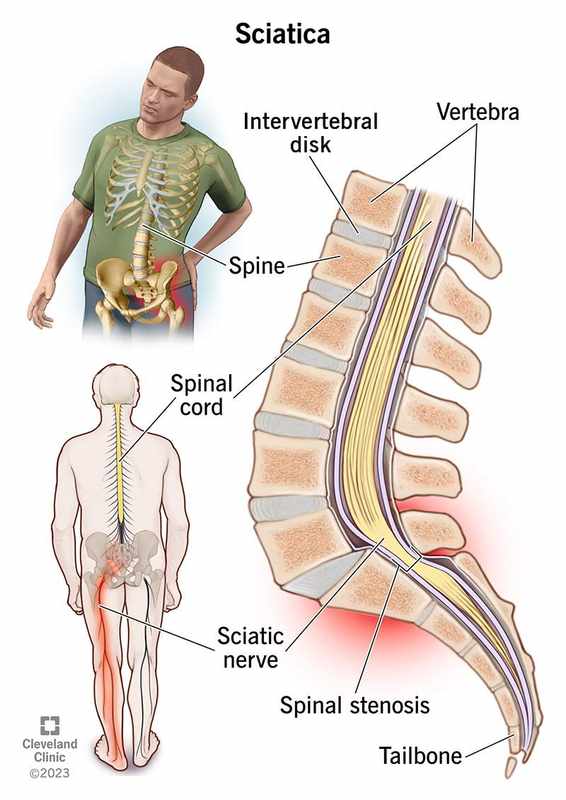
In our previous section, we explored the intriguing connection between neurological disorders and low back pain. Now, let’s dive deeper into the world of anti-seizure medications and examine whether they can truly ease low back pain.
The Mechanisms Behind Anti-Seizure Medications
Anti-seizure medications, such as gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica), work by modulating the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. These chemicals play a crucial role in regulating pain perception, mood, and cognitive function. By altering the levels of these neurotransmitters, anti-seizure medications can help reduce the abnormal electrical activity that contributes to seizures.
But how do these medications relate to low back pain? Research suggests that they may be effective in treating certain types of chronic pain, including low back pain. The exact mechanisms are still not fully understood, but several theories have been proposed:
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Anti-seizure medications may help reduce inflammation and swelling in the affected area, which can contribute to pain.
- Pain modulation: By altering neurotransmitter levels, these medications may modulate pain signals sent from the spinal cord to the brain, reducing their intensity or frequency.
- Central sensitization: Anti-seizure medications may help desensitize overactive pain pathways in the central nervous system, making it easier for the brain to filter out irrelevant pain signals.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Anti-Seizure Medications for Low Back Pain
While anti-seizure medications may offer a new treatment approach for low back pain, they are not without potential drawbacks:
- Risks of addiction: Gabapentin and pregabalin have been linked to addiction in some cases.
- Sedation side effects: These medications can cause drowsiness or fatigue, which may impact daily activities.
- Limited scientific evidence: While promising, the available research is limited, and more studies are needed to fully understand their effectiveness and potential risks.
As with any medication, it’s essential to weigh the potential benefits against the potential drawbacks and discuss treatment options with a healthcare professional. They can help determine whether anti-seizure medications might be an effective treatment for your low back pain.
Next Steps: Exploring the Future of Anti-Seizure Medications in Low Back Pain Treatment
In our next section, we’ll delve into the current state of research on anti-seizure medications and low back pain. We’ll examine ongoing studies, potential applications, and what this might mean for the future of chronic pain treatment.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: Seizures and Epilepsy American Journal of Neuroradiology: Gabapentin for chronic low back painGet Expert Advice on Low Back Pain
Don’t let chronic pain hold you back. Consult with a medical expert today.
Consult with a Medical ExpertIn the previous sections of this blog post, we’ve explored the connection between neurological disorders and low back pain, as well as the potential benefits of anti-seizure medications in treating chronic low back pain.
Key Points Covered So Far
We’ve learned that:
- Lower back pain affects over 80% of adults at some point in their lives.
- Research has shown a significant link between neurological disorders like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease, and chronic low back pain.
- Anti-seizure medications may have potential benefits in treating low back pain due to their mechanisms of action and the shared underlying pathology between neurological conditions and chronic low back pain.
Final Insights
While anti-seizure medications show promise in addressing low back pain, it’s essential to note that each individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. As with any medication or treatment approach, a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the best course of action.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while anti-seizure medications may offer a new avenue of exploration for individuals seeking relief from chronic low back pain, it’s crucial to prioritize evidence-based research and thorough evaluations. As we continue to uncover the complexities of the human body, we may uncover even more innovative approaches to addressing this pervasive condition.
Remember, you are not alone in your struggle with low back pain. By staying informed, seeking professional guidance, and exploring innovative solutions, you can take control of your health and wellbeing.