Your immune system is a complex and fascinating network of cells, proteins, and tissues that work together to keep you healthy. Among the various types of white blood cells, monocytes play a crucial role in fighting off infections and inflammation. But have you ever wondered what’s considered “normal” when it comes to absolute monocyte counts?
What is Absolute Monocyte Count?
Absolute monocyte count, also known as total monocyte count or absolute monocyte number (AMN), refers to the actual number of monocytes present in a given volume of blood. This measurement is important because it can help diagnose and monitor various conditions, such as infections, inflammatory disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
Why is Absolute Monocyte Count Important?
Absolute monocyte count is an essential parameter for evaluating the immune system’s response to infections and inflammation. For instance, a low absolute monocyte count may indicate impaired immune function or compromised host defense against pathogens, while a high count could suggest excessive inflammation or immune activation.
What is the Normal Range for Absolute Monocytes?
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the normal range for absolute monocytes and explore what’s considered “normal” in terms of these vital white blood cells. Stay tuned as we examine the significance of this measurement and its implications for our understanding of immune function and overall health.

Your immune system is a complex and fascinating network of cells, proteins, and tissues that work together to keep you healthy. Among the various types of white blood cells, monocytes play a crucial role in fighting off infections and inflammation. But have you ever wondered what’s considered “normal” when it comes to absolute monocyte counts?
What is Absolute Monocyte Count?
Absolute monocyte count, also known as total monocyte count or absolute monocyte number (AMN), refers to the actual number of monocytes present in a given volume of blood. This measurement is important because it can help diagnose and monitor various conditions, such as infections, inflammatory disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
Why is Absolute Monocyte Count Important?
Absolute monocyte count is an essential parameter for evaluating the immune system’s response to infections and inflammation. For instance, a low absolute monocyte count may indicate impaired immune function or compromised host defense against pathogens, while a high count could suggest excessive inflammation or immune activation.
What is the Normal Range for Absolute Monocytes?
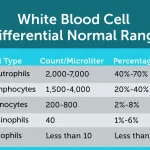
The normal range for absolute monocytes varies depending on age, sex, and health status. According to the American Society of Clinical Pathology (ASCP), a normal absolute monocyte count for adults ranges from 0.1 to 0.7 x 10^9/L (or 100 to 700 cells per microliter). For children, the range is typically higher, with a normal absolute monocyte count ranging from 0.2 to 2.5 x 10^9/L (or 200 to 2,500 cells per microliter).
It’s essential to note that these ranges are general guidelines and may vary depending on the laboratory performing the test or specific clinical context. For instance, a low absolute monocyte count in a patient with chronic inflammation might be considered normal if it’s within the range expected for someone with their condition.
Factors Affecting Absolute Monocyte Count
A variety of factors can influence absolute monocyte counts, including:
- Age: Monocyte counts tend to increase with age.
- Sex: Men generally have higher monocyte counts than women.
- Infections: Certain infections, such as sepsis or HIV/AIDS, can cause increased monocyte production.
- Inflammatory disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus may lead to elevated monocyte counts due to chronic inflammation.
- Autoimmune diseases: Some autoimmune disorders, like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, can result in altered monocyte counts.
Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate interpretation of absolute monocyte counts and effective patient care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the normal range for absolute monocytes is a vital parameter for evaluating immune function and diagnosing various conditions. By considering age, sex, health status, and other influencing factors, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into a patient’s immune response and develop targeted treatment strategies.
Stay tuned for our next installment, where we’ll delve deeper into the significance of absolute monocyte counts and explore their role in various medical contexts.
Get Expert Consultation
Consult with medical and health experts to gain a deeper understanding of absolute monocytes.
Start chatYour immune system is a complex and fascinating network of cells, proteins, and tissues that work together to keep you healthy. Among the various types of white blood cells, monocytes play a crucial role in fighting off infections and inflammation. But have you ever wondered what’s considered “normal” when it comes to absolute monocyte counts?
What is Absolute Monocyte Count?
Absolute monocyte count, also known as total monocyte count or absolute monocyte number (AMN), refers to the actual number of monocytes present in a given volume of blood. This measurement is important because it can help diagnose and monitor various conditions, such as infections, inflammatory disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
Why is Absolute Monocyte Count Important?
Absolute monocyte count is an essential parameter for evaluating the immune system’s response to infections and inflammation. For instance, a low absolute monocyte count may indicate impaired immune function or compromised host defense against pathogens, while a high count could suggest excessive inflammation or immune activation.
What is the Normal Range for Absolute Monocytes?
In healthy adults, the normal range for absolute monocytes typically falls between 100-700 cells per microliter (μL). However, this value can vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and health status. For instance, children may have higher absolute monocyte counts than adults, while individuals with certain medical conditions may have lower or higher counts.
Now that we’ve explored the normal range for absolute monocytes, it’s essential to summarize our key points:
- Absolute monocyte count refers to the actual number of monocytes present in a given volume of blood.
- This measurement is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring various conditions, including infections, inflammatory disorders, and autoimmune diseases.
- In healthy adults, the normal range for absolute monocytes typically falls between 100-700 cells per μL.
As we’ve seen, understanding the normal range for absolute monocytes is vital for evaluating immune function and overall health. By recognizing what’s considered “normal” in terms of these vital white blood cells, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat various conditions, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the normal range for absolute monocytes serves as a valuable indicator of immune system function and overall health. As we continue to learn more about the intricacies of our immune systems, it’s essential to appreciate the significance of this measurement in diagnosing and managing various conditions. By staying informed about what’s considered “normal” when it comes to absolute monocytes, you’ll be better equipped to maintain optimal health and well-being.
Read the Case Study MC Roy Aerospace on Page 332 and Answer Questions 4 and 5 on Page 333: Are you looking for a challenge? Dive into this intriguing case study and put your skills to the test by answering the thought-provoking questions. Perfect for those who love to learn and grow.
I Just Adore You Asking for More: Are you a fan of romance? Get swept away by this heartwarming tale of love and connection. Discover the joy of giving and receiving when someone asks for more.