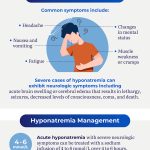
As you step into the world of blood tests, you might have come across a term that seems quite foreign to your everyday life – Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN). It’s not uncommon for people to feel perplexed when faced with unfamiliar medical jargon. But don’t worry, we’re here to demystify this concept and help you understand what a normal BUN range means.
What is Blood Urea Nitrogen?
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is a type of blood test that measures the amount of waste product in your blood. It’s often used to diagnose or monitor kidney function, as well as detect potential issues with liver function. But what does it really mean when your BUN levels are out of whack?
Why Does it Matter?
Understanding a normal BUN range is crucial for several reasons:
- It helps diagnose and monitor kidney disease, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.
- It’s an important indicator of liver function, as the liver plays a critical role in processing waste products.
- Abnormal BUN levels can also indicate dehydration, malnutrition, or other underlying medical conditions.
In this post, we’ll dive deeper into what constitutes a normal BUN range and what it means for your overall health. Stay tuned!
To better understand what a normal BUN range means, let’s first explore how BUN levels are affected by kidney function.
Kidney Function and BUN Levels
Your kidneys play a vital role in removing waste products from your blood. When your kidneys aren’t functioning properly, these waste products can build up in your bloodstream, leading to increased BUN levels. For example:
- A person with chronic kidney disease may have elevated BUN levels due to their kidneys’ inability to efficiently remove waste products.
- Someone who has experienced acute kidney injury (AKI) may also have high BUN levels as a result of the damage caused to their kidneys.
This highlights the importance of monitoring BUN levels in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as creatinine, to gain a comprehensive understanding of your overall kidney function.
What Factors Affect BUN Levels?
A range of factors can influence BUN levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming a diet high in protein or low in fluids can increase BUN levels.
- Certain medications: Diuretics, certain antibiotics, and other medications can affect BUN levels.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain conditions, such as liver disease, diabetes, or heart failure, can impact BUN levels.
It’s essential to consider these factors when interpreting your BUN results to ensure an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
What is a Normal BUN Range?
A normal BUN range varies depending on age, sex, and other factors. Generally:
- In adults, the normal BUN range is 7-20 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
- In children, the normal BUN range is typically lower, ranging from 2-17 mg/dL.
It’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to determine what constitutes a normal BUN range for you based on your individual factors.
We’ve covered the importance of understanding a normal BUN range and explored how various factors can influence BUN levels. In our next segment, we’ll delve into the potential causes of abnormal BUN levels and discuss what steps you can take to address them. Stay tuned!
Learn more about normal BUN levels Discover the facts and statistics surrounding chronic kidney diseaseConsult a Medical & Health Expert
Get expert advice on blood urea nitrogen levels and how they relate to your overall health.
Start chatIn our previous discussion, we explored what Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) is, its importance in diagnosing and monitoring kidney and liver function, and how abnormal levels can indicate underlying medical conditions. Now, let’s summarize the key points covered so far:
Summary
- BUN measures the amount of waste product in your blood.
- A normal BUN range is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring kidney disease, liver function, and detecting potential underlying medical conditions.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s take a step back and reflect on what it all means:
Final Insights
A normal BUN range is not just a number – it’s a window into your overall health. By understanding what constitutes a healthy BUN level, you can take proactive steps to maintain your kidney and liver function, and potentially avoid serious complications.
As we conclude this post, remember that a normal BUN range is a vital indicator of your body’s internal workings. By staying informed and taking control of your health, you can empower yourself to make informed decisions about your care and well-being. So, the next time you receive the results of a BUN test, don’t be perplexed – be empowered! A normal BUN range is just the beginning of a healthier, happier you.