A trip to the doctor’s office often leaves us feeling anxious and uncertain about our health, especially when we receive test results that seem unclear or concerning.
Low CO2 Blood Test Results: What Do They Mean?
If you’ve recently had a blood test and received results indicating low carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, you’re likely wondering what it means for your health. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the significance of low CO2 blood test results, exploring their possible causes, symptoms, and implications for your well-being.
What Is Carbon Dioxide in the Blood?
Before we dive into the meaning of low CO2 blood test results, it’s essential to understand what carbon dioxide is and its role in our bodies. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, produced when our cells break down glucose for energy. In a normal physiological process, CO2 is transported to the lungs via the bloodstream, where it’s exhaled out.
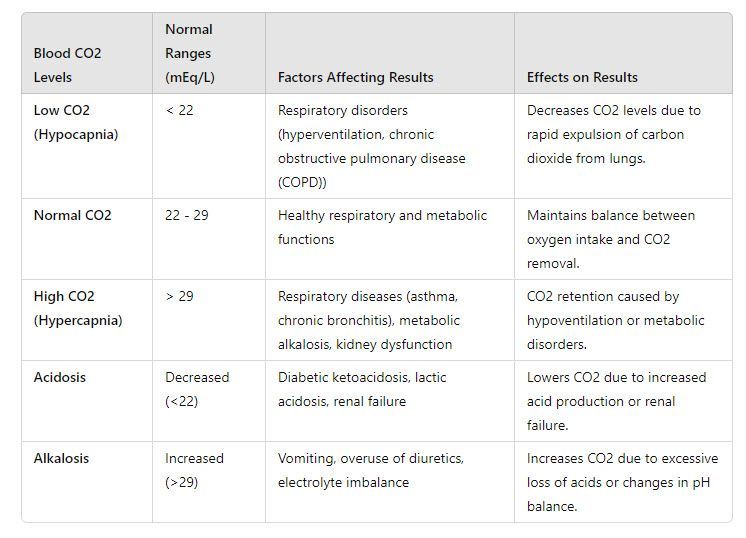
In healthy individuals, the average CO2 levels in arterial blood range from 35-45 mmHg (millimeters of mercury). However, when CO2 levels drop below this range, it can indicate various underlying conditions that require medical attention. In the next section, we’ll explore some possible causes of low CO2 blood test results and what you can do to address them.
A trip to the doctor’s office often leaves us feeling anxious and uncertain about our health, especially when we receive test results that seem unclear or concerning.
Low CO2 Blood Test Results: What Do They Mean?
If you’ve recently had a blood test and received results indicating low carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, you’re likely wondering what it means for your health. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the significance of low CO2 blood test results, exploring their possible causes, symptoms, and implications for your well-being.
What Is Carbon Dioxide in the Blood?
Before we dive into the meaning of low CO2 blood test results, it’s essential to understand what carbon dioxide is and its role in our bodies. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, produced when our cells break down glucose for energy. In a normal physiological process, CO2 is transported to the lungs via the bloodstream, where it’s exhaled out.
In healthy individuals, the average CO2 levels in arterial blood range from 35-45 mmHg (millimeters of mercury). However, when CO2 levels drop below this range, it can indicate various underlying conditions that require medical attention. In the next section, we’ll explore some possible causes of low CO2 blood test results and what you can do to address them.
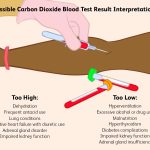
Possible Causes of Low CO2 Blood Test Results
There are several reasons why your CO2 levels might be low. Here are a few potential causes:
Respiratory acidosis, where the buildup of excess CO2 in the bloodstream can cause low CO2 levels.
Cardiac conditions, such as congestive heart failure or cardiogenic shock, which can lead to reduced CO2 levels.
Pulmonary embolism or pulmonary edema, where blood clots or fluid accumulation in the lungs can impede CO2 transport.
Severe anemia or blood loss, which can reduce the amount of oxygen available to support cellular metabolism and increase CO2 production.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, a complication of uncontrolled diabetes where the body produces high levels of ketones, leading to low CO2 levels.
It’s essential to note that these are just a few potential causes of low CO2 blood test results. Your healthcare provider will likely perform additional tests and evaluations to determine the underlying cause of your low CO2 levels.
What Can You Do if You Have Low CO2 Blood Test Results?
If you’ve been diagnosed with low CO2 blood test results, it’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to address any underlying conditions. This may involve:
Medications or treatments for underlying cardiac or pulmonary conditions.
Blood transfusions or oxygen therapy if anemia or blood loss is the cause.
Changes to your diet and exercise routine, including increased physical activity and a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
We’ll continue exploring the implications of low CO2 blood test results in our next section. Stay tuned!
Get Expert Advice on Low CO2 Blood Test Results
Our medical and health experts are here to help you understand the implications of low CO2 blood test results. Schedule a consultation today!
Schedule a consultationA trip to the doctor’s office often leaves us feeling anxious and uncertain about our health, especially when we receive test results that seem unclear or concerning.
Low CO2 Blood Test Results: What Do They Mean?
If you’ve recently had a blood test and received results indicating low carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, you’re likely wondering what it means for your health. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the significance of low CO2 blood test results, exploring their possible causes, symptoms, and implications for your well-being.
What Is Carbon Dioxide in the Blood?
Before we dive into the meaning of low CO2 blood test results, it’s essential to understand what carbon dioxide is and its role in our bodies. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, produced when our cells break down glucose for energy. In a normal physiological process, CO2 is transported to the lungs via the bloodstream, where it’s exhaled out.
In healthy individuals, the average CO2 levels in arterial blood range from 35-45 mmHg (millimeters of mercury). However, when CO2 levels drop below this range, it can indicate various underlying conditions that require medical attention. In the next section, we’ll explore some possible causes of low CO2 blood test results and what you can do to address them.
What Causes Low CO2 Blood Test Results?
The primary cause of low CO2 blood test results is usually related to respiratory or metabolic disorders. Some potential underlying conditions include:
- Pneumonia or other lung infections
- Asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Respiratory acidosis, a condition characterized by abnormally high levels of carbon dioxide in the blood
- Metabolic disorders such as diabetes or hypothyroidism
- Kidney disease or respiratory failure
It’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of your low CO2 blood test results. They may order additional tests, such as a blood gas analysis or lung function tests, to help diagnose and treat any underlying conditions.
What Can You Do If You Have Low CO2 Blood Test Results?
If you’ve been diagnosed with low CO2 blood test results, it’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan. Depending on the underlying cause of your condition, this may include:
- Medications to manage respiratory or metabolic disorders
- Oxygen therapy to increase oxygen levels in your bloodstream
- Pulmonary rehabilitation to improve lung function and overall health
- Dietary changes to better manage blood sugar or thyroid hormone levels, if applicable
Remember that low CO2 blood test results are not a normal part of the aging process. It’s essential to address any underlying conditions promptly to prevent complications and improve your overall quality of life.
A Call to Action: Taking Control of Your Health
If you’ve recently received low CO2 blood test results, it’s time to take control of your health. By working closely with your healthcare provider and making necessary lifestyle changes, you can effectively manage any underlying conditions and improve your overall well-being.
Remember that your health is a journey, not a destination. Take the first step today by scheduling an appointment with your doctor and discussing your test results in detail. With the right treatment plan and support system in place, you can achieve optimal health and live the life you deserve.