As medical professionals and patients alike continue to grapple with the complexities of autoimmune diseases, one lesser-known yet crucial aspect deserves closer examination: High Anion Gap Autoimmune (HAGA). In this comprehensive overview, we’ll delve into the intricacies of HAGA, exploring its definition, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
A Mystery Wrapped in Enigma
For years, medical professionals have struggled to pinpoint the exact causes behind HAGA. This rare autoimmune disorder affects an estimated 1 in 100,000 individuals worldwide, with women being disproportionately affected. Despite its relatively low incidence, HAGA’s profound impact on patients’ quality of life cannot be overstated.
The Anion Gap Enigma
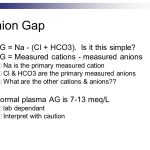
At the heart of HAGA lies an aberrant anion gap – a critical aspect of blood chemistry that regulates electrolyte balance. Essentially, the anion gap represents the difference between positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). In healthy individuals, this gap is relatively narrow, ensuring proper ion exchange and fluid balance.
However, in HAGA patients, the anion gap widens significantly, leading to a cascade of symptoms. Imagine a delicate equilibrium being disrupted – the consequences are far-reaching and often devastating for those affected. As we explore the intricacies of HAGA, it’s essential to recognize the profound implications this disorder has on patients’ daily lives.

As we continue our exploration of High Anion Gap Autoimmune (HAGA), it’s essential to understand the intricate relationship between the anion gap and the body’s delicate balance. The widening of the anion gap is not a standalone phenomenon, but rather a symptom of a broader autoimmune disorder.
Autoimmune Responses Gone Awry
In HAGA, the immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues, leading to a misdirected inflammatory response. This aberrant response causes the anion gap to widen, disrupting electrolyte balance and fluid homeostasis. The consequences are far-reaching, affecting various bodily systems and functions.
Symptoms of High Anion Gap Autoimmune
The manifestations of HAGA can be diverse and unpredictable, making diagnosis a challenging task. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and malaise
- Muscle weakness and cramping
- Cardiac arrhythmias and palpitations
- Nephrotoxicity and kidney damage
- Polyuria (excessive urine production)
It’s crucial to note that HAGA can present with a range of severity, from mild to life-threatening. Patients may experience symptoms that seem unrelated or appear suddenly, making timely diagnosis and treatment critical.
Diagnosing HAGA often requires a combination of laboratory tests, medical imaging, and clinical evaluation. Key diagnostic markers include:
- Anion gap calculation (typically > 16 mEq/L)
- Serum electrolyte levels (e.g., sodium, potassium, bicarbonate)
- Renal function tests (e.g., blood urea nitrogen, creatinine)
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) or echocardiogram to assess cardiac function
A comprehensive diagnostic approach is essential for accurate HAGA diagnosis. Healthcare providers should consider the patient’s medical history, physical examination findings, and laboratory results to establish a definitive diagnosis.
Effective treatment and management of HAGA often require collaboration among specialists, including nephrologists, cardiologists, and endocrinologists. Treatment strategies may include:
- Fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy
- Cardiac medications (e.g., beta blockers) to manage arrhythmias
- Renal function monitoring and management
- Corticosteroid therapy to reduce inflammation
- Lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise changes
A personalized treatment plan is crucial for addressing the complex needs of HAGA patients. Further research is needed to develop more targeted and effective therapies.
As we conclude this overview of High Anion Gap Autoimmune, it’s essential to acknowledge the significant impact this disorder has on patients’ lives. By understanding the intricacies of HAGA, healthcare providers can work towards developing more effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. In our next installment, we’ll delve into the latest research and findings in the field of HAGA.
Learn more about autoimmune disorders at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)Expert Consultation: Consult with Medical & Health Experts
Get personalized guidance on High Anion Gap Autoimmune and related health topics from our network of medical professionals.
Start chatIn this comprehensive overview of High Anion Gap Autoimmune (HAGA), we’ve explored the definition, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this rare autoimmune disorder.
Summing Up the Key Points
To recap, HAGA is a complex condition characterized by an aberrant anion gap in blood chemistry. This widening of the anion gap leads to a range of symptoms including fatigue, muscle weakness, and electrolyte imbalances. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of laboratory tests, including serum electrolytes and anion gap measurements.
Treatment approaches for HAGA often involve immunosuppressive therapies and lifestyle modifications aimed at managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. While there is currently no cure for HAGA, early detection and intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Final Insights
HAGA serves as a poignant reminder of the complexities and mysteries that still surround autoimmune disorders. As medical professionals continue to unravel the intricacies of this condition, it’s essential to acknowledge the profound impact HAGA has on patients’ quality of life. By promoting awareness and understanding, we can work towards developing more effective treatment strategies and ultimately improve patient care.
A Call to Action
As we conclude this comprehensive overview of High Anion Gap Autoimmune, it’s clear that there is still much to be learned about this enigmatic disorder. As medical professionals and patients alike continue to navigate the complexities of HAGA, let us remain steadfast in our commitment to advancing knowledge and improving patient care. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by this devastating condition.
Recommended Reads:
- The Estimating Problem on Page 734 and Then Answer the Questions on Page 735: Are you struggling to estimate accurately? Dive into this article to learn how to tackle complex problems and boost your confidence in estimation. Plus, get answers to common questions that can help you improve your skills.
- Symptoms of Fatty Liver Due to Alcohol Consumption: If you’re a heavy drinker, it’s crucial to know the signs of fatty liver disease. This article breaks down the symptoms and warning signs, helping you stay on top of your health and make informed choices.
- What is Anemia Caused by Folic Acid Deficiency?: Discover the link between folic acid deficiency and anemia. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options to help you overcome this condition.