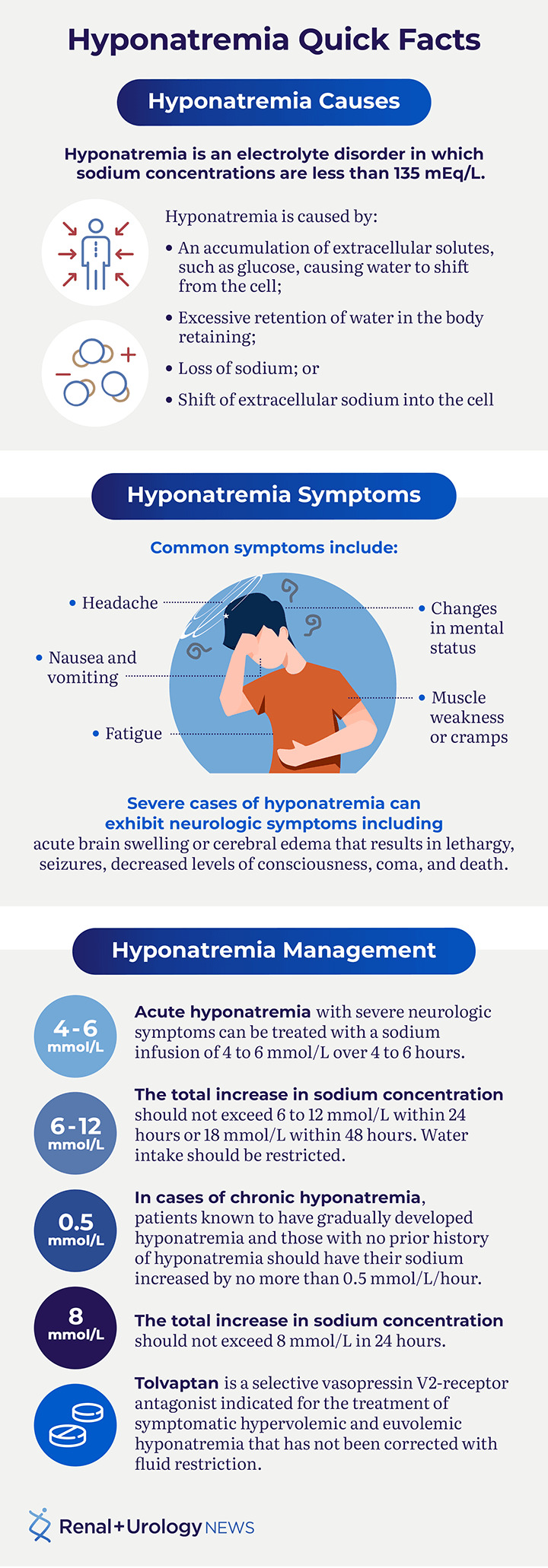
Your body’s blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels are crucial for maintaining proper bodily functions. When these levels get out of balance, it can lead to a range of issues that affect your overall health. In this blog post, we’ll be exploring the causes of low blood sodium (< 135 mmol/L) accompanied by high urea nitrogen (> 18 mg/dL). But before we dive into the details, let’s set the stage.
The Importance of Blood Sodium and Urea Nitrogen
When it comes to maintaining proper bodily functions, blood sodium levels play a critical role. Sodium helps regulate the amount of water in your body, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure, nerve function, and muscle contractions. On the other hand, urea nitrogen is a waste product that’s removed from the bloodstream through urination. When these two levels get out of balance, it can lead to complications ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
The Interplay Between Blood Sodium and Urea Nitrogen
So, what happens when blood sodium drops while urea nitrogen rises? In most cases, this occurs due to an underlying medical condition or a combination of factors. One key factor is the kidneys’ ability to regulate both sodium reabsorption and urea excretion. When the kidneys are impaired or overwhelmed, it can lead to changes in blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels. For instance:
Your body’s blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels are crucial for maintaining proper bodily functions. When these levels get out of balance, it can lead to a range of issues that affect your overall health. In this blog post, we’ll be exploring the causes of low blood sodium (< 135 mmol/L) accompanied by high urea nitrogen (> 18 mg/dL). But before we dive into the details, let’s set the stage.
The Importance of Blood Sodium and Urea Nitrogen
When it comes to maintaining proper bodily functions, blood sodium levels play a critical role. Sodium helps regulate the amount of water in your body, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure, nerve function, and muscle contractions. On the other hand, urea nitrogen is a waste product that’s removed from the bloodstream through urination. When these two levels get out of balance, it can lead to complications ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions.
The Interplay Between Blood Sodium and Urea Nitrogen
So, what happens when blood sodium drops while urea nitrogen rises? In most cases, this occurs due to an underlying medical condition or a combination of factors. One key factor is the kidneys’ ability to regulate both sodium reabsorption and urea excretion. When the kidneys are impaired or overwhelmed, it can lead to changes in blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels. For instance:
- Kidney disease: Conditions like chronic kidney disease (CKD), acute kidney injury (AKI), or nephrotic syndrome can disrupt normal kidney function, leading to altered blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels.
- Dehydration: Severe dehydration can cause a sudden drop in blood sodium levels, while urea nitrogen may rise due to the kidneys’ inability to effectively remove waste products.
- Circulatory disorders: Certain circulatory conditions like heart failure or peripheral artery disease (PAD) can impair kidney function and lead to changes in blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels.
- Endocrine disorders: Hormonal imbalances, such as those seen in adrenal insufficiency or hyperaldosteronism, can affect sodium reabsorption and urea excretion by the kidneys.
These conditions can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. For example, patients with low blood sodium levels may experience muscle weakness, fatigue, or seizures, while those with high urea nitrogen levels may exhibit signs of kidney failure, such as nausea, vomiting, or decreased urine output.
The Bottom Line
When it comes to the interplay between blood sodium and urea nitrogen, understanding the underlying causes is crucial. Whether due to a medical condition, lifestyle factors, or a combination of both, recognizing these connections can help healthcare professionals provide more effective treatment and management strategies for patients with low blood sodium and high urea nitrogen levels.
Learn more about kidney failure and how it can impact blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels.
Expert Consultation for Blood Sodium Low + Urea Nitrogen High
Get personalized guidance from medical and health experts to understand your test results better.
Consult an ExpertIn conclusion, when blood sodium levels drop below 135 mmol/L while urea nitrogen rises above 18 mg/dL, it’s essential to identify and address the underlying cause. This may involve treating an underlying medical condition, such as heart failure or kidney disease, or modifying lifestyle habits like diet and fluid intake. By understanding the interplay between blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels, you can take proactive steps to maintain overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
The key points covered in this blog post are:
- Blood sodium levels play a crucial role in regulating bodily functions, including blood pressure, nerve function, and muscle contractions.
- Urea nitrogen is a waste product removed from the bloodstream through urination, with high levels indicating potential kidney or liver dysfunction.
- The kidneys regulate both sodium reabsorption and urea excretion, and impaired kidney function can lead to changes in blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels.
- A combination of factors, including medical conditions, lifestyle habits, and environmental influences, can contribute to imbalances in blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels.
Final Insights
In today’s fast-paced world, it’s easy to overlook the importance of maintaining proper bodily functions. By recognizing the interconnectedness of blood sodium and urea nitrogen levels, you can take a proactive approach to your health and well-being. Remember that small changes, such as adjusting your diet or increasing fluid intake, can have a significant impact on overall health.
Low iron saturation: a critical health indicator: Did you know that low iron levels can indicate underlying health issues? Discover the importance of monitoring your iron saturation and what it means for your overall well-being.
Average core body temperature: Ever wondered what’s considered a normal body temperature? Explore the average core body temperature and how it impacts your daily life, from physical performance to mental clarity.