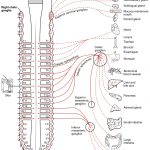
Have you ever felt like your body is on high alert, ready to respond to any perceived threat? Maybe it’s a sudden noise, a surprise from behind, or an intense workout. When this happens, your body’s “fight or flight” response kicks in, and it can be both exhilarating and exhausting.
Activation of the Sympathetic Branch of the Autonomic Nervous System Results In…
In this blog post, we’ll dive into what happens when the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system is activated. You might be wondering why this matters. Well, understanding how our body’s “fight or flight” response works can have significant implications for our physical and mental well-being.
The Importance of Autonomic Nervous System Function
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for controlling many of our bodily functions without us even thinking about them. It’s divided into two main branches: the sympathetic branch, which activates the “fight or flight” response, and the parasympathetic branch, which promotes relaxation and restoration.
When the sympathetic branch is activated, it triggers a cascade of physiological responses that prepare our body for action. In this section, we’ll explore what happens when this occurs. So, let’s get started!
When the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system is activated, it sets off a chain reaction that prepares our body for action. This includes a surge of energy and alertness, as well as changes to our cardiovascular, respiratory, and metabolic systems.
The Physiological Effects of Sympathetic Activation
One of the most notable effects is the increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This prepares our circulatory system for increased oxygen delivery to our muscles, allowing us to respond quickly to the perceived threat. Our respiratory system also gets a boost, with faster and deeper breathing to take in more oxygen.
In addition, the sympathetic branch releases stress hormones like adrenaline (also known as epinephrine) and cortisol, which further amplify our body’s response. This can lead to physical symptoms such as:
- Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat)
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Sweating
- Muscle tension
The sympathetic branch also suppresses our digestive system, releasing stomach acid and slowing down digestion to redirect resources to the “fight or flight” response. This can lead to symptoms such as:
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
- Changes in bowel movements
It’s worth noting that the sympathetic branch is also responsible for our body’s natural response to exercise. When we’re engaging in physical activity, our sympathetic branch helps us tap into our inner athlete, increasing our energy and performance.
The Impact of Chronic Sympathetic Activation
While acute activation of the sympathetic branch can be beneficial for short-term stress or exercise, chronic activation can have negative effects on our overall health. Prolonged periods of stress can lead to:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Cardiovascular disease
- Mood disorders like anxiety and depression
- Weakened immune system
To learn more about how to manage chronic stress and balance your autonomic nervous system, check out this article on the National Institute of Mental Health’s website: Stress.
In our next section, we’ll explore the importance of parasympathetic activation and how it can help counterbalance the effects of chronic sympathetic dominance.
Get Expert Medical Guidance
Activate your sympathetic branch and unlock the secrets of autonomic nervous system. Consult with medical experts for a deeper understanding.
Start chatIn part one of our exploration of the autonomic nervous system, we’ve delved into what happens when the sympathetic branch is activated. To recap, activation of this branch results in a range of physiological responses that prepare our body for action.
Recap: The Sympathetic Branch’s Response
When the sympathetic branch is triggered, it sets off a chain reaction that includes:
- Rapid heartbeat and increased blood pressure
- Pupils dilating to allow more light into the eyes
- Release of stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol
- Increased glucose release in preparation for energy demands
- Reduced digestion and peripheral circulation to redirect resources to core functions
This suite of responses enables us to react quickly and efficiently to perceived threats, whether physical or emotional. However, chronic activation of the sympathetic branch can lead to negative consequences, such as anxiety and fatigue.
Final Insights: Balancing the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Branches
Achieving a healthy balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches is crucial for overall well-being. By understanding how our autonomic nervous system functions, we can take steps to regulate its activity and foster a sense of calm and resilience.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Autonomic Nervous System
In conclusion, the sympathetic branch’s activation is a vital response that enables us to respond to threats. However, it’s equally important to recognize the importance of the parasympathetic branch in promoting relaxation and restoration.
By acknowledging the interplay between these two branches, we can take steps to cultivate greater awareness and control over our autonomic nervous system. This knowledge empowers us to make conscious choices that promote overall health, vitality, and emotional resilience.
Balanitis vs Herpes: A Picture Comparison of Penis Issues: Ever wondered what sets balanitis apart from herpes? Explore this informative article, featuring striking visuals and expert insights to help you diagnose and treat these common penis issues with confidence!
What is 1 Bilirubin in Dog Urine: A Comprehensive Guide: Are you concerned about your furry friend’s urine test results? Get to the bottom of what a 1 bilirubin reading really means for your dog’s health. This expert guide covers everything from causes to treatments, so you can take control of your pup’s well-being.