A sudden change in your body’s chemistry can have significant consequences on your overall health. And when it comes to blood sugar levels, even a slight deviation from the normal range can have far-reaching implications.
Abnormally High Concentration of Glucose in the Blood: Understanding Hyperglycemia
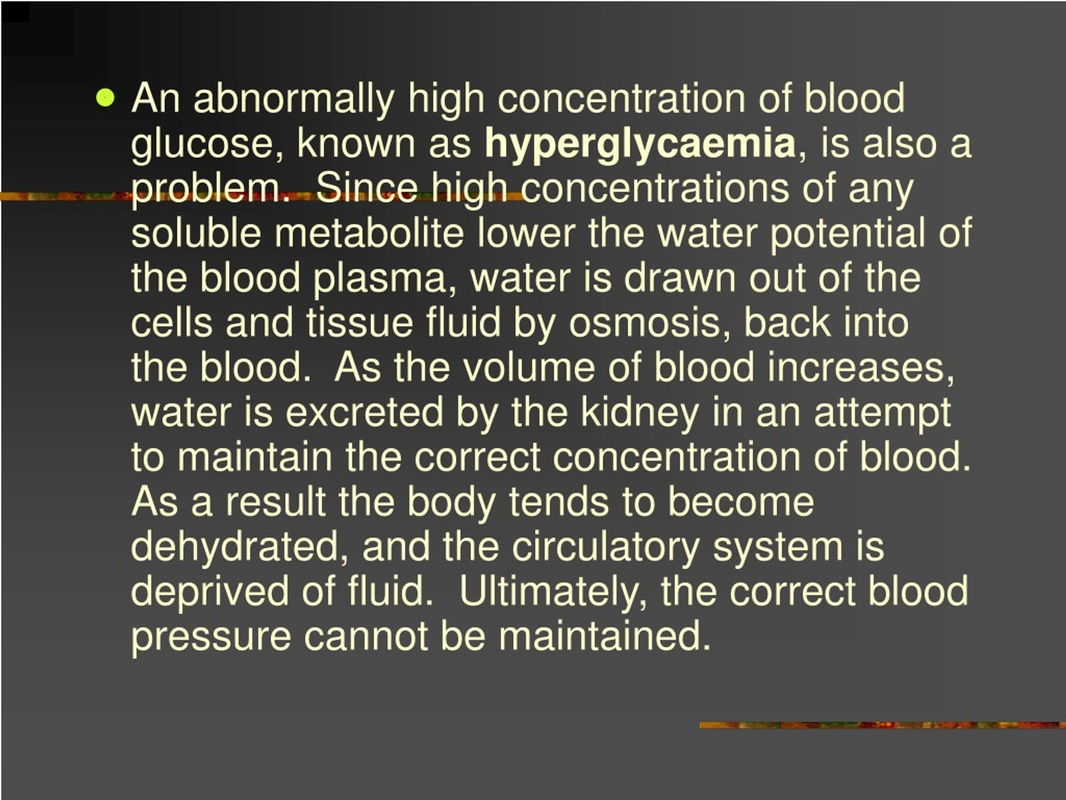
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of hyperglycemia, a condition characterized by abnormally high concentrations of glucose in the blood. This condition can have serious consequences if left untreated or unmanaged.
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hypoglycemia, its counterpart with low blood sugar levels, is more commonly discussed and recognized. However, hyperglycemia is equally important to understand, as it affects millions of people worldwide. In a nutshell, hyperglycemia occurs when the body’s glucose regulation system malfunctions, resulting in an excessive amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream.
The normal range for blood sugar levels varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and medical conditions. For healthy individuals without diabetes, a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level below 100 mg/dL is considered normal. However, this threshold can fluctuate in people with underlying health issues or taking certain medications.
A sudden change in your body’s chemistry can have significant consequences on your overall health. And when it comes to blood sugar levels, even a slight deviation from the normal range can have far-reaching implications.
Abnormally High Concentration of Glucose in the Blood: Understanding Hyperglycemia
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of hyperglycemia, a condition characterized by abnormally high concentrations of glucose in the blood. This condition can have serious consequences if left untreated or unmanaged.
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hypoglycemia, its counterpart with low blood sugar levels, is more commonly discussed and recognized. However, hyperglycemia is equally important to understand, as it affects millions of people worldwide. In a nutshell, hyperglycemia occurs when the body’s glucose regulation system malfunctions, resulting in an excessive amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream.
The normal range for blood sugar levels varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and medical conditions. For healthy individuals without diabetes, a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level below 100 mg/dL is considered normal. However, this threshold can fluctuate in people with underlying health issues or taking certain medications.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
When left untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to a range of symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Blurred vision
- Skin infections or slow-healing cuts
- Weakened immune system
- Ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition characterized by high levels of ketones in the blood
If left untreated, hyperglycemia can also increase the risk of developing long-term complications, such as:
- Nephropathy (kidney damage)
- Retinopathy (eye damage)
- Neuropathy (nerve damage)
Fortunately, hyperglycemia is a manageable condition. By understanding the underlying causes and symptoms, individuals can take steps to prevent or reverse its effects.
Treatment Options for Hyperglycemia
The treatment approach often depends on the underlying cause of hyperglycemia. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: Metformin, sulfonylureas, and thiazolidinediones are commonly used to manage blood sugar levels.
- Dietary changes: A balanced diet low in refined carbohydrates and added sugars can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, stress management, and weight loss (if necessary) can also contribute to improved glucose regulation.
For those living with diabetes, managing hyperglycemia is crucial. According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), tight glycemic control can reduce the risk of long-term complications by up to 50%.
Learn more about diabetes management from the American Diabetes AssociationConclusion
In this blog post, we’ve explored the world of hyperglycemia and its implications on overall health. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for hyperglycemia, individuals can take steps to prevent or manage this condition effectively.
In our next installment, we’ll delve into the role of nutrition in regulating blood sugar levels and discuss strategies for incorporating healthy eating habits into daily life.
Expert Consultation for High Blood Sugar
Are you concerned about the risks associated with abnormally high concentration of glucose in your blood? Our medical experts are here to provide personalized guidance and support.
Consult with an expertA sudden change in your body’s chemistry can have significant consequences on your overall health. And when it comes to blood sugar levels, even a slight deviation from the normal range can have far-reaching implications.
Abnormally High Concentration of Glucose in the Blood: Understanding Hyperglycemia
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of hyperglycemia, a condition characterized by abnormally high concentrations of glucose in the blood. This condition can have serious consequences if left untreated or unmanaged.
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hypoglycemia, its counterpart with low blood sugar levels, is more commonly discussed and recognized. However, hyperglycemia is equally important to understand, as it affects millions of people worldwide. In a nutshell, hyperglycemia occurs when the body’s glucose regulation system malfunctions, resulting in an excessive amount of glucose circulating in the bloodstream.
The normal range for blood sugar levels varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and medical conditions. For healthy individuals without diabetes, a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level below 100 mg/dL is considered normal. However, this threshold can fluctuate in people with underlying health issues or taking certain medications.
Key Takeaways
So far, we’ve explored the basics of hyperglycemia, including its definition and prevalence. To recap, here are the key points:
- Hyperglycemia is characterized by abnormally high concentrations of glucose in the blood.
- The normal range for blood sugar levels varies depending on individual factors.
- Hyperglycemia can have serious consequences if left untreated or unmanaged.
Final Insights
If you’re concerned about your blood sugar levels, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help determine the underlying cause of hyperglycemia and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Remember, early detection and management are crucial in preventing long-term complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hyperglycemia is a condition that requires attention and understanding. By recognizing the signs and symptoms, we can take proactive steps to manage this condition and prevent its devastating consequences. As we wrap up this blog post, remember that small changes today can lead to a healthier tomorrow.
The Ultimate Guide to Intermittent Fasting for Women: Are you looking for a way to boost your energy levels and improve your overall health? Intermittent fasting may be the answer! Check out our comprehensive guide to learn how women can benefit from this popular diet trend.
I Just Adore You Asking for More: Ever wondered why people ask for more when it comes to love? Dive into the world of relationships and discover the secrets behind this fascinating phenomenon.