In the world of medicine, understanding the difference between benign and malignant is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Yet, many people are still unclear about what these terms mean, and how they can impact their health.
What’s the Difference?
As we explore this topic, you may be wondering why it matters so much. The truth is, knowing whether a growth or tumor is benign or malignant can have life-altering consequences. Malignant tumors, in particular, can spread quickly and be highly aggressive, requiring prompt and effective treatment.
The Benign Option
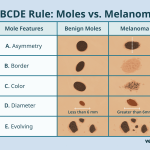
A benign growth or tumor is non-cancerous and typically does not invade surrounding tissues. These types of growths are often harmless and may even go unnoticed until they become large enough to cause symptoms. An example of a benign condition is a skin mole, which can be removed without causing harm to the surrounding tissue.
In this section, we will delve deeper into the characteristics and implications of benign conditions, including what you can expect during diagnosis and treatment. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, understanding the difference between benign and malignant is essential for making informed decisions about your health.
In the world of medicine, understanding the difference between benign and malignant is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Yet, many people are still unclear about what these terms mean, and how they can impact their health.
What’s the Difference?
As we explore this topic, you may be wondering why it matters so much. The truth is, knowing whether a growth or tumor is benign or malignant can have life-altering consequences. Malignant tumors, in particular, can spread quickly and be highly aggressive, requiring prompt and effective treatment.
The Benign Option
A benign growth or tumor is non-cancerous and typically does not invade surrounding tissues. These types of growths are often harmless and may even go unnoticed until they become large enough to cause symptoms. An example of a benign condition is a skin mole, which can be removed without causing harm to the surrounding tissue.
Benign conditions can also be characterized by slow growth rates, well-defined borders, and no ability to spread to other parts of the body. For instance, uterine fibroids are a common type of benign tumor that affects women’s reproductive health. In most cases, these tumors do not require treatment unless they cause symptoms or interfere with fertility.
Another key characteristic of benign conditions is their lack of genetic mutations. Unlike malignant tumors, which often have specific genetic abnormalities that drive their growth and spread, benign tumors typically develop through abnormal cell proliferation rather than genetic changes.
Malignant Tumors: A More Serious Affair
A malignant tumor, on the other hand, is a type of cancerous growth that can invade surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body. These tumors are typically characterized by rapid growth rates, irregular borders, and an ability to metastasize to distant organs.
Malignant tumors often have specific genetic mutations that drive their growth and progression. For example, breast cancer is a type of malignant tumor that can be driven by genetic mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
It’s essential to note that while benign tumors are generally non-life-threatening, some may still require treatment if they cause symptoms or affect surrounding tissues. Conversely, malignant tumors often require prompt and aggressive treatment to prevent further spread and improve patient outcomes.
In the next section, we’ll explore the diagnostic approaches used to distinguish between benign and malignant tumors, as well as the implications for patients and healthcare providers.
Consult a Medical Expert Today!
If you have questions or concerns about benign vs malignant conditions, our medical experts are here to help.
Consult a Medical ExpertIn the world of medicine, understanding the difference between benign and malignant is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Yet, many people are still unclear about what these terms mean, and how they can impact their health.
What’s the Difference?
As we explore this topic, you may be wondering why it matters so much. The truth is, knowing whether a growth or tumor is benign or malignant can have life-altering consequences. Malignant tumors, in particular, can spread quickly and be highly aggressive, requiring prompt and effective treatment.
The Benign Option
A benign growth or tumor is non-cancerous and typically does not invade surrounding tissues. These types of growths are often harmless and may even go unnoticed until they become large enough to cause symptoms. An example of a benign condition is a skin mole, which can be removed without causing harm to the surrounding tissue.
In this section, we will delve deeper into the characteristics and implications of benign conditions, including what you can expect during diagnosis and treatment. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or healthcare professional, understanding the difference between benign and malignant is essential for making informed decisions about your health.
Summarizing the Key Points
In summary, the main differences between benign and malignant conditions are:
- Benevolent growths do not invade surrounding tissues, whereas malignant tumors can spread quickly and aggressively.
- Benevolent conditions are typically non-cancerous, while malignant tumors have the potential to cause significant harm if left untreated.
It is crucial to understand these differences in order to make informed decisions about your health. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of benign and malignant conditions, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Final Insights
In conclusion, understanding the difference between benign and malignant is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment. Whether you’re facing a benign or malignant condition, it is crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan of action.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment can greatly impact the outcome of any health issue. By staying informed and proactive, you can take control of your health and well-being.
More Health Insights:
- Chills common side effects of taking Cipro: Did you know that Cipro, a powerful antibiotic, can cause chills as one of its most common side effects? Click to learn more about the potential risks and how to manage them.
- Symptoms of fatty liver due to alcohol consumption: If you’re a heavy drinker, it’s essential to know the signs of fatty liver disease. From pain and fatigue to nausea and vomiting, learn how to identify these symptoms and take control of your health.
- What is anemia caused by folic acid deficiency: Folic acid plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells. When you’re deficient, it can lead to anemia. Discover how to recognize the signs and take steps to prevent this condition.