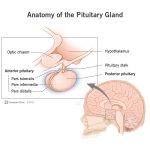
The pituitary gland is often referred to as the “master gland” due to its critical role in regulating various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, and reproductive processes. While all hormones produced by the pituitary gland are essential, the anterior part of the pituitary gland plays a particularly significant role in controlling various physiological processes. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of anterior pituitary gland hormones and explore their functions, effects, and importance.
The Importance of Anterior Pituitary Gland Hormones
Anterior pituitary gland hormones are responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, reproductive processes, and stress response. These hormones play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring the body’s physiological processes run smoothly and efficiently.
Growth Hormone (GH)
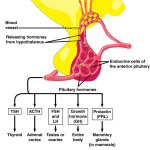
One of the most well-known anterior pituitary gland hormones is growth hormone (GH). Produced by somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland, GH stimulates cell reproduction and differentiation, promoting growth and development throughout life. In children and adolescents, GH plays a critical role in regulating height and weight, while in adults, it helps maintain muscle mass and bone density.
Insufficient production of GH can lead to growth hormone deficiency (GHD), resulting in stunted growth and physical development. Conversely, excessive GH levels can cause gigantism, leading to abnormal growth and developmental abnormalities. The delicate balance of GH levels is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
The pituitary gland is often referred to as the “master gland” due to its critical role in regulating various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, and reproductive processes. While all hormones produced by the pituitary gland are essential, the anterior part of the pituitary gland plays a particularly significant role in controlling various physiological processes. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of anterior pituitary gland hormones and explore their functions, effects, and importance.
The Importance of Anterior Pituitary Gland Hormones
Anterior pituitary gland hormones are responsible for regulating various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, reproductive processes, and stress response. These hormones play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, ensuring the body’s physiological processes run smoothly and efficiently.
Growth Hormone (GH)
One of the most well-known anterior pituitary gland hormones is growth hormone (GH). Produced by somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland, GH stimulates cell reproduction and differentiation, promoting growth and development throughout life. In children and adolescents, GH plays a critical role in regulating height and weight, while in adults, it helps maintain muscle mass and bone density.
Insufficient production of GH can lead to growth hormone deficiency (GHD), resulting in stunted growth and physical development. Conversely, excessive GH levels can cause gigantism, leading to abnormal growth and developmental abnormalities. The delicate balance of GH levels is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Prolactin
Prolactin is another important anterior pituitary gland hormone, primarily produced by lactotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. While prolactin’s primary function is associated with lactation during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it also plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses and modulating stress.
High levels of prolactin have been linked to various disorders, including galactorrhea (abnormal milk production) and hyperprolactinemia (excessive prolactin levels). Conversely, low prolactin levels can result in hypoprolactinemia, which may be associated with impaired lactation or infertility.
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is another essential anterior pituitary gland hormone, produced by thyrotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are crucial for regulating metabolism.
A deficiency in TSH production can lead to hypothyroidism, characterized by fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance. Conversely, excessive TSH levels can result in hyperthyroidism, marked by rapid heartbeat, sweating, and weight loss.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is a vital anterior pituitary gland hormone, produced by corticotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, which helps regulate stress responses and metabolism.
A deficiency in ACTH production can lead to Addison’s disease, characterized by fatigue, weight loss, and hyperpigmentation. Conversely, excessive ACTH levels can result in Cushing’s syndrome, marked by obesity, hypertension, and glucose intolerance.
Conclusion
The anterior part of the pituitary gland plays a critical role in regulating various physiological processes, including growth and development, metabolism, reproductive processes, and stress response. The hormones produced by this region, such as GH, prolactin, TSH, and ACTH, are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
In our next blog post, we will explore the posterior part of the pituitary gland and its role in regulating bodily functions. Stay tuned!
Expert Consultation
Discuss your anterior pituitary gland hormone questions with medical professionals.
Consult an ExpertIn conclusion, anterior pituitary gland hormones play a vital role in regulating various bodily functions, including growth and development, metabolism, reproductive processes, and stress response. Growth hormone (GH), in particular, is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being, with its effects ranging from promoting physical growth in children to maintaining muscle mass and bone density in adults.
As we’ve explored the significance of anterior pituitary gland hormones, it’s clear that their balance is crucial for ensuring homeostasis. Any imbalance can have far-reaching consequences, highlighting the importance of understanding these hormones and how they interact with other bodily systems.
The anterior part of the pituitary gland is a fascinating and complex system, and this blog post has provided an overview of its key functions and effects. By recognizing the importance of anterior pituitary gland hormones, we can better appreciate the intricate mechanisms that govern our bodies and strive for optimal health and wellness.
In summary, the key points covered in this blog post are:
- The anterior part of the pituitary gland plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions.
- Anterior pituitary gland hormones, such as growth hormone (GH), are essential for maintaining homeostasis and overall health and well-being.
- Growth hormone (GH) stimulates cell reproduction and differentiation, promoting growth and development throughout life.
We hope this blog post has provided a valuable insight into the world of anterior pituitary gland hormones. Remember that understanding your body’s physiological processes is essential for maintaining optimal health and wellness.
Ask a CPA: Your Free Online Questionnaire: Need financial advice but don’t know where to start? Our free online CPAs are here to help. Get instant answers to your burning questions and take control of your finances.
What is Clobetasol Propionate Cream: A Comprehensive Guide: Are you struggling with skin conditions like psoriasis or eczema? Learn about the benefits and uses of clobetasol propionate cream, a powerful topical medication. Find out what it’s used for and how to use it effectively.