The world of medication is a complex and ever-evolving one, with new treatments and dosages emerging all the time. But what happens when a once-effective medication no longer works as intended? For patients suffering from chronic conditions, this can be a daunting prospect – especially when it comes to medications that have been their lifeline for years.
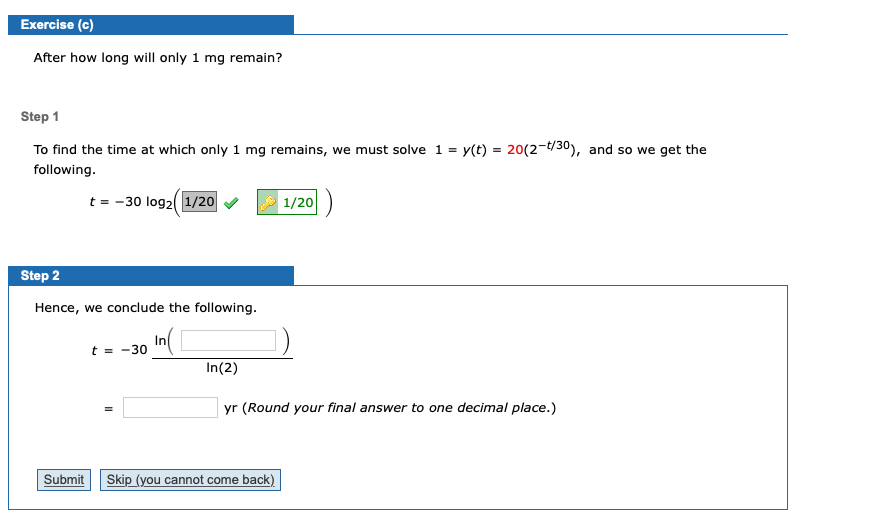
After How Long Will Only 1 MG Remain?
In this blog post, we’ll be exploring the trend of dwindling medication efficacy and what it means for patients. From understanding why medications stop working as well as they once did to discussing the potential consequences of a world where only tiny doses remain effective – we’ll delve into the ins and outs of this pressing issue.
Why Medication Efficacy Matters
Medications are often the backbone of treatment for chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and depression. When these medications stop working as well as they once did, patients may be left struggling to manage their symptoms, leading to a decrease in quality of life. But why does this happen? Let’s take a closer look.
The answer lies in the complex interplay between pharmacokinetics (the study of how our bodies absorb and process medications) and pharmacodynamics (the study of how medications interact with our bodies). As we’ll explore further, factors like increased resistance, changed metabolism, and altered dosing can all contribute to a medication’s effectiveness dwindling over time.
The world of medication is a complex and ever-evolving one, with new treatments and dosages emerging all the time. But what happens when a once-effective medication no longer works as intended? For patients suffering from chronic conditions, this can be a daunting prospect – especially when it comes to medications that have been their lifeline for years.
After How Long Will Only 1 MG Remain?
In this blog post, we’ll be exploring the trend of dwindling medication efficacy and what it means for patients. From understanding why medications stop working as well as they once did to discussing the potential consequences of a world where only tiny doses remain effective – we’ll delve into the ins and outs of this pressing issue.
Why Medication Efficacy Matters
Medications are often the backbone of treatment for chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and depression. When these medications stop working as well as they once did, patients may be left struggling to manage their symptoms, leading to a decrease in quality of life. But why does this happen? Let’s take a closer look.
The answer lies in the complex interplay between pharmacokinetics (the study of how our bodies absorb and process medications) and pharmacodynamics (the study of how medications interact with our bodies). As we’ll explore further, factors like increased resistance, changed metabolism, and altered dosing can all contribute to a medication’s effectiveness dwindling over time.
Increased Resistance: A Growing Concern
One major factor contributing to the decline in medication efficacy is the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. As antibiotics are overused or misused, bacteria adapt by developing resistance, making them less effective against infections. This phenomenon has been seen with medications like ampicillin and penicillin, where patients may require higher doses or alternative treatments.
A study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy found that antibiotic resistance rates have increased significantly over the past few decades, highlighting the need for more targeted treatment strategies and the importance of preserving antibiotic effectiveness (1).
Metabolic Changes: A Hidden Factor
Another factor influencing medication efficacy is metabolic changes. As we age or experience certain health conditions, our metabolism can slow down, leading to altered absorption rates and reduced medication effectiveness. For instance, older adults may require adjusted dosing for medications like warfarin due to changes in their liver function (2).
Altered Dosing: The Impact of Age and Weight
In addition to metabolic changes, age and weight can also impact medication efficacy. As patients age, their body composition may change, affecting the way medications are absorbed and processed. Similarly, significant changes in weight can alter medication effectiveness, requiring adjusted dosing or alternative treatments.
What’s Next?
In our next installment, we’ll be exploring the potential consequences of a world where only tiny doses remain effective for certain medications. From discussing the implications on healthcare systems to examining the role of personalized medicine in addressing these challenges – we’ll delve into the complex and evolving landscape of medication efficacy.
Expert Insights on Medication Effects
We are ready to answer your questions, day or night.
Start chatThe world of medication is a complex and ever-evolving one, with new treatments and dosages emerging all the time. But what happens when a once-effective medication no longer works as intended? For patients suffering from chronic conditions, this can be a daunting prospect – especially when it comes to medications that have been their lifeline for years.
After How Long Will Only 1 MG Remain?
In this blog post, we’ll be exploring the trend of dwindling medication efficacy and what it means for patients. From understanding why medications stop working as well as they once did to discussing the potential consequences of a world where only tiny doses remain effective – we’ll delve into the ins and outs of this pressing issue.
Why Medication Efficacy Matters
Medications are often the backbone of treatment for chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and depression. When these medications stop working as well as they once did, patients may be left struggling to manage their symptoms, leading to a decrease in quality of life. But why does this happen? Let’s take a closer look.
The answer lies in the complex interplay between pharmacokinetics (the study of how our bodies absorb and process medications) and pharmacodynamics (the study of how medications interact with our bodies). As we’ll explore further, factors like increased resistance, changed metabolism, and altered dosing can all contribute to a medication’s effectiveness dwindling over time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the decline of medication efficacy is a pressing issue that affects patients worldwide. As we move forward, it’s crucial that we continue to research and develop new treatments that address this trend. By understanding the complexities of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, we can work towards creating medications that remain effective for years to come. It’s time to take action and ensure that patients receive the treatment they deserve – not just 1mg.
The ultimate guide to intermittent fasting for women: Are you looking for a weight loss strategy that actually works? This comprehensive guide will walk you through the benefits, tips, and tricks of intermittent fasting specifically designed for women. Learn how to boost your energy, improve your mental clarity, and achieve your health goals with this powerful dieting technique!
The estimating problem on page 734 and then answer the questions on page 735: Are you struggling to solve a math problem that has got you stumped? This article will guide you through the solution, providing step-by-step instructions and real-world examples. Don’t let math anxiety hold you back – unlock your problem-solving skills today!