A peculiar phenomenon has been observed in some medical laboratories, sparking curiosity and intrigue among healthcare professionals worldwide. The topic is Specific Gravity Urine 1.20 – a seemingly innocuous finding that warrants closer examination.
The Enigma of Specific Gravity Urine 1.20
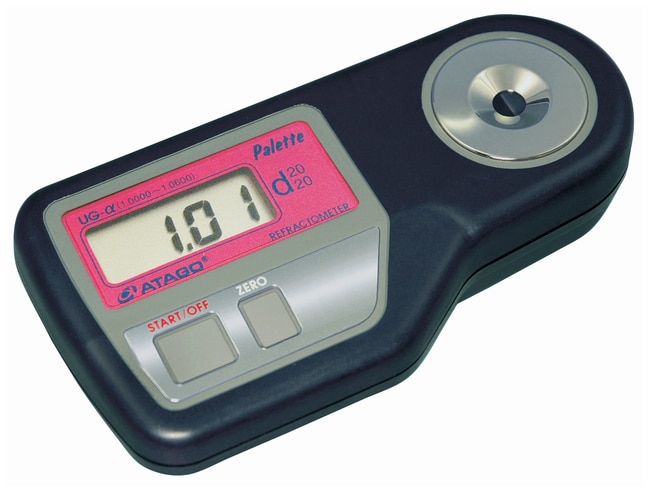
Specific gravity (SG) is a fundamental concept in urinalysis, measuring the density of urine relative to water. A normal SG value ranges from 1.005 to 1.030, with slight variations depending on factors like age, sex, and hydration status. However, in some cases, the SG value may deviate significantly, such as when it reaches an astonishing 1.20.
What Does Specific Gravity Urine 1.20 Signify?
SG urine 1.20 is often seen in patients with certain medical conditions or on specific medications. This anomaly can be an indicator of underlying abnormalities, such as kidney damage or impaired urinary concentrating ability. In this section, we will delve into the possible causes and implications of this unusual finding, providing a solid foundation for further exploration.
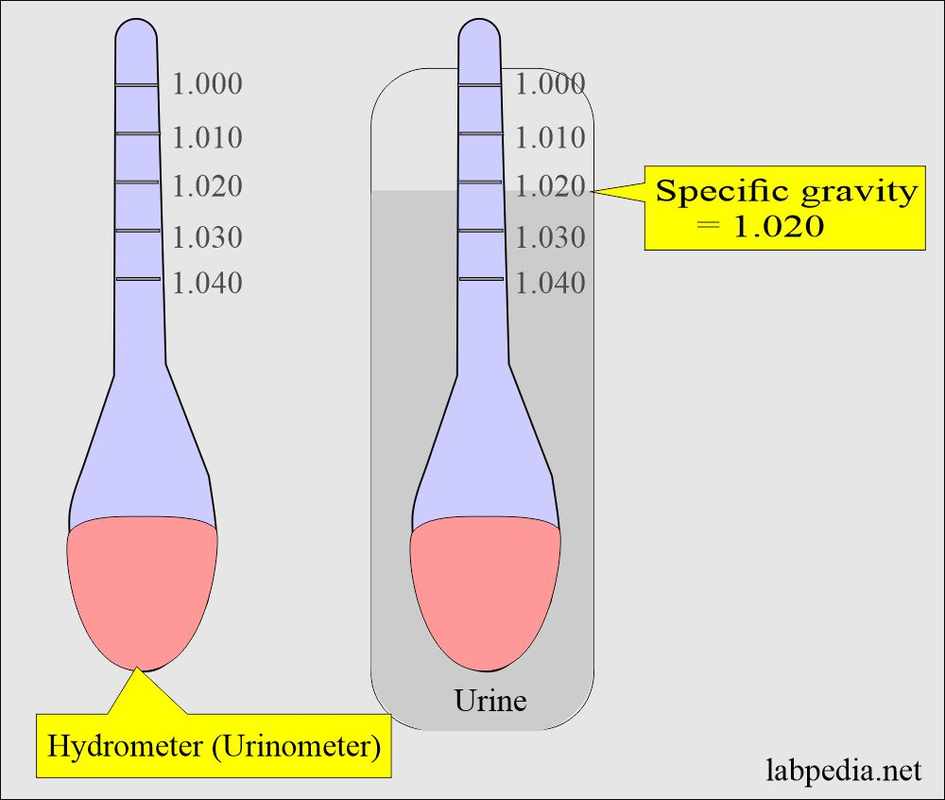
A peculiar phenomenon has been observed in some medical laboratories, sparking curiosity and intrigue among healthcare professionals worldwide. The topic is Specific Gravity Urine 1.20 – a seemingly innocuous finding that warrants closer examination.
The Enigma of Specific Gravity Urine 1.20
Specific gravity (SG) is a fundamental concept in urinalysis, measuring the density of urine relative to water. A normal SG value ranges from 1.005 to 1.030, with slight variations depending on factors like age, sex, and hydration status. However, in some cases, the SG value may deviate significantly, such as when it reaches an astonishing 1.20.
What Does Specific Gravity Urine 1.20 Signify?
SG urine 1.20 is often seen in patients with certain medical conditions or on specific medications. This anomaly can be an indicator of underlying abnormalities, such as kidney damage or impaired urinary concentrating ability. For instance, individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD) may exhibit elevated SG values due to the kidneys’ reduced capacity to concentrate urine.
Another possible cause is the use of diuretics, which are medications that increase urine production and can lead to abnormally high SG readings. Certain medications like furosemide (Lasix) and hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) are known to cause increased urine output and may contribute to an SG value of 1.20.
It is essential for healthcare professionals to be aware of these possible causes and to consider the patient’s medical history, current medications, and other relevant factors when interpreting SG values. A thorough examination of the urinalysis report, including the presence of proteinuria, hematuria, or casts, can help identify underlying conditions.
Furthermore, it is crucial for laboratory personnel to ensure proper collection and handling procedures are followed to minimize errors and artifacts that could affect the accuracy of the SG measurement. This includes adequate specimen labeling, proper storage, and timely analysis.
What’s Next?
In our next section, we will explore the implications of Specific Gravity Urine 1.20 in more depth, discussing its relationship to other laboratory tests and clinical findings. We’ll also examine the potential consequences of neglecting or misinterpreting this finding, highlighting the importance of proper evaluation and follow-up.
Learn more about urinalysis at Mayo Clinic Discover more about urinalysis tests on Lab Tests OnlineExpert Consultation for Urine Specific Gravity
Get personalized guidance from medical experts. Whether you have questions or concerns about your urine specific gravity, we’re here to help.
Start chatIn conclusion, the phenomenon of Specific Gravity Urine 1.20 is more than just an intriguing curiosity – it holds significant implications for patient care and diagnosis. As we’ve explored the possible causes and implications of this unusual finding, it’s clear that SG urine 1.20 requires further investigation and attention from healthcare professionals.
The takeaways are clear: when encountered with a Specific Gravity Urine value of 1.20, healthcare providers should consider the possibility of underlying kidney damage or impaired urinary concentrating ability. Further testing and evaluation may be necessary to determine the root cause of this anomaly and develop an effective treatment plan for the patient.
As we continue to uncover the mysteries of urinalysis and its role in diagnosing and managing various medical conditions, it’s essential that we stay vigilant and proactive in addressing unusual findings like Specific Gravity Urine 1.20. By doing so, we can provide patients with the best possible care and improve health outcomes.
The Average Resting Heart Rate for Teenage Girls: Are you curious about the normal heart rate range for teenage girls? This article delves into the average resting heart rate for this age group, helping you better understand your body’s rhythm. Read on to discover more!
What is 1 Bilirubin in Dog Urine: A Comprehensive Guide: Got concerns about your furry friend’s health? This informative guide breaks down the meaning of 1 bilirubin in dog urine, providing valuable insights for pet owners. Dive into this must-read article to empower yourself with knowledge!