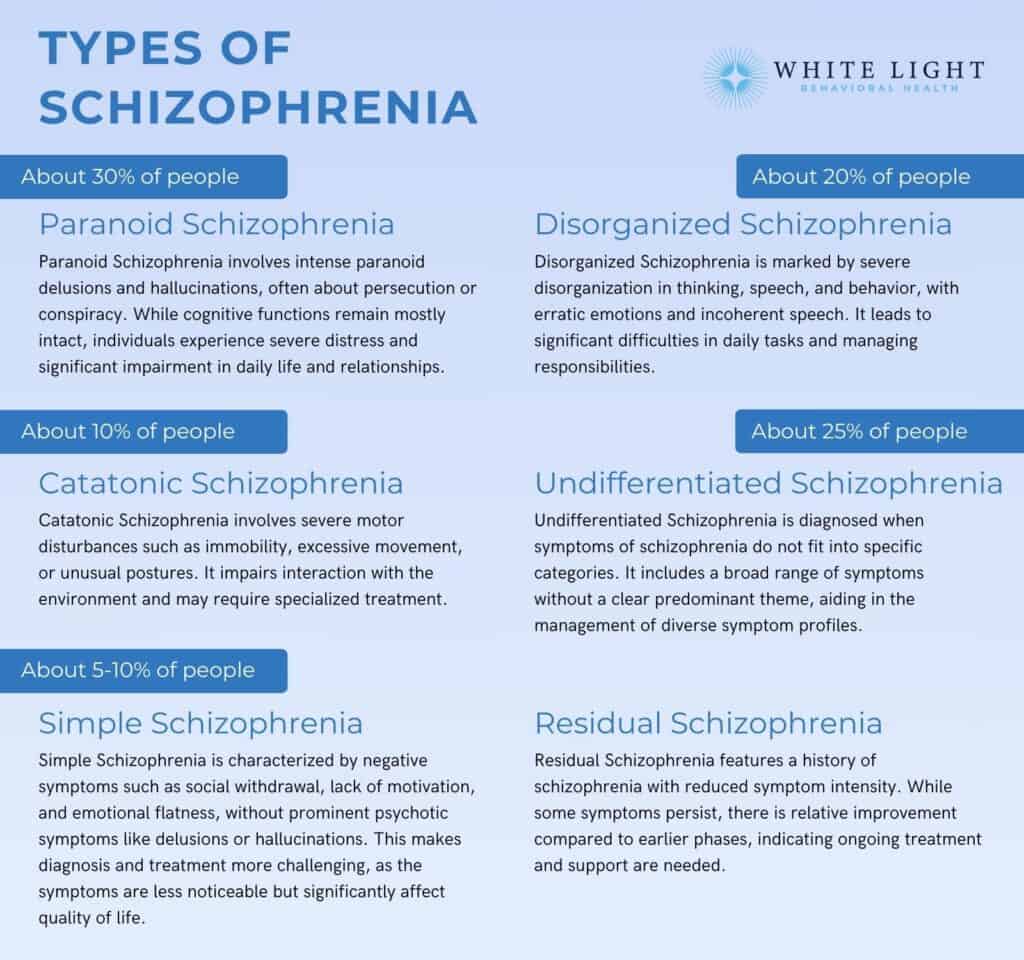
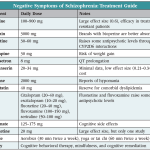
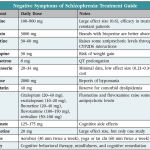
In the complex and often mysterious world of mental health, few conditions are as shrouded in misconception and stigma as schizophrenia. This debilitating brain disorder affects over 21 million people worldwide, yet it remains a topic of whispered conversations and hazy understanding.
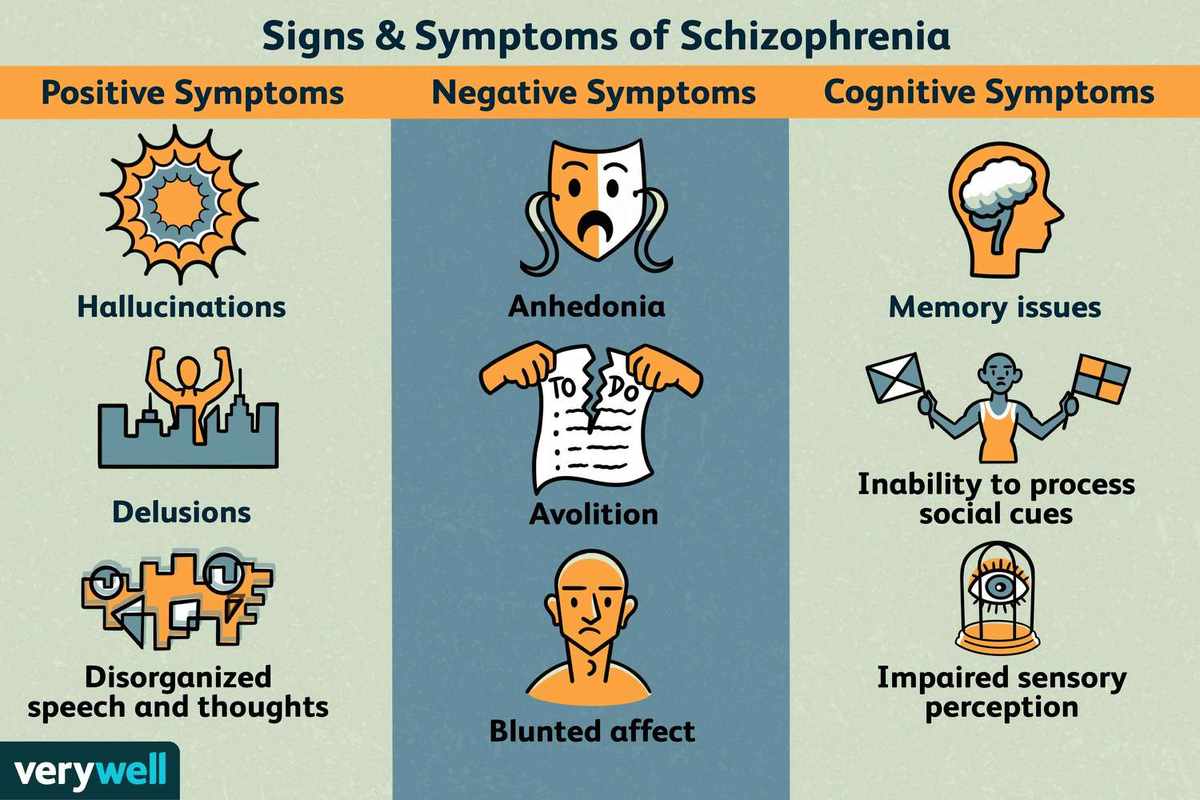
3 Categories of Schizophrenia Symptoms: Positive, Negative, and Disorganized
As we strive to raise awareness and promote understanding, it’s essential to clarify the various symptoms that characterize this condition. One crucial aspect is the categorization of schizophrenia symptoms into three distinct categories: positive, negative, and disorganized.
The Importance of Categorizing Schizophrenia Symptoms
By recognizing these different symptom patterns, mental health professionals can better diagnose and treat individuals with schizophrenia. Moreover, understanding the nuances of each category can help reduce stigma and promote empathy for those affected.
So, let’s dive into the first key aspect: Positive Symptoms.
Positive Symptoms
Positive symptoms are characterized by excesses or abnormalities in cognitive, emotional, or behavioral processes. These symptoms can be distressing and impair daily functioning. Examples of positive symptoms include:
- Hallucinations (hearing, seeing, tasting, smelling, or feeling things that aren’t there)
- Delusions (firm beliefs in things that are not true)
- Catatonia (a state of extreme rigidity or immobility)
In the next section, we’ll explore Negative Symptoms and their significance in understanding schizophrenia.
In the complex and often mysterious world of mental health, few conditions are as shrouded in misconception and stigma as schizophrenia. This debilitating brain disorder affects over 21 million people worldwide, yet it remains a topic of whispered conversations and hazy understanding.
3 Categories of Schizophrenia Symptoms: Positive, Negative, and Disorganized
As we strive to raise awareness and promote understanding, it’s essential to clarify the various symptoms that characterize this condition. One crucial aspect is the categorization of schizophrenia symptoms into three distinct categories: positive, negative, and disorganized.
The Importance of Categorizing Schizophrenia Symptoms
By recognizing these different symptom patterns, mental health professionals can better diagnose and treat individuals with schizophrenia. Moreover, understanding the nuances of each category can help reduce stigma and promote empathy for those affected.
So, let’s dive into the first key aspect: Positive Symptoms.
Positive Symptoms
Positive symptoms are characterized by excesses or abnormalities in cognitive, emotional, or behavioral processes. These symptoms can be distressing and impair daily functioning. Examples of positive symptoms include:
- Hallucinations (hearing, seeing, tasting, smelling, or feeling things that aren’t there)
- Delusions (firm beliefs in things that are not true)
- Catatonia (a state of extreme rigidity or immobility)
It’s essential to note that positive symptoms can be challenging for both the individual experiencing them and their loved ones. For instance, hallucinations can lead to feelings of fear, anxiety, or disorientation, while delusions can cause individuals to become withdrawn or isolated.
In some cases, positive symptoms may be more pronounced than others, making it crucial for mental health professionals to carefully assess each individual’s unique presentation. By doing so, they can develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of the individual with schizophrenia.
Negative Symptoms
Now, let’s move on to Negative Symptoms.
Negative symptoms are characterized by a decrease or absence of normal emotional, cognitive, and behavioral processes. These symptoms can be just as debilitating as positive symptoms, as they often lead to social withdrawal, apathy, and depression. Examples of negative symptoms include:
- Apathy (lack of interest or motivation)
- Anhedonia (loss of pleasure or enjoyment in activities)
- Affective flattening (reduced emotional expression)
Understanding negative symptoms is crucial for developing effective treatment plans. For instance, cognitive-behavioral therapy can help individuals with schizophrenia address apathy and anhedonia by increasing motivation and pleasure in activities.
We’ll explore Disorganized Symptoms next, which are just as vital to understanding this complex condition.
Learn more about schizophrenia from the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)Expert Consultation for Schizophrenia
If you or someone you know is struggling with schizophrenia, our medical experts are here to provide guidance and support.
Consult a medical expert nowIn the complex and often mysterious world of mental health, few conditions are as shrouded in misconception and stigma as schizophrenia. This debilitating brain disorder affects over 21 million people worldwide, yet it remains a topic of whispered conversations and hazy understanding.
3 Categories of Schizophrenia Symptoms: Positive, Negative, and Disorganized
As we strive to raise awareness and promote understanding, it’s essential to clarify the various symptoms that characterize this condition. One crucial aspect is the categorization of schizophrenia symptoms into three distinct categories: positive, negative, and disorganized.
The Importance of Categorizing Schizophrenia Symptoms
By recognizing these different symptom patterns, mental health professionals can better diagnose and treat individuals with schizophrenia. Moreover, understanding the nuances of each category can help reduce stigma and promote empathy for those affected.
So, let’s dive into the first key aspect: Positive Symptoms.
Positive Symptoms
Positive symptoms are characterized by excesses or abnormalities in cognitive, emotional, or behavioral processes. These symptoms can be distressing and impair daily functioning. Examples of positive symptoms include:
- Hallucinations (hearing, seeing, tasting, smelling, or feeling things that aren’t there)
- Delusions (firm beliefs in things that are not true)
- Catatonia (a state of extreme rigidity or immobility)
In the next section, we’ll explore Negative Symptoms and their significance in understanding schizophrenia.
Recap: The Three Categories of Schizophrenia Symptoms
We’ve covered the first two categories: Positive and Negative. Let’s quickly summarize:
- Positive symptoms: characterized by excesses or abnormalities in cognitive, emotional, or behavioral processes (hallucinations, delusions, catatonia)
- Negative symptoms: characterized by decreases or absences of normal functions (apathy, flattened emotions, social withdrawal)
Now, let’s move on to the third category: Disorganized Symptoms.
Disorganized Symptoms
Disorganized symptoms are characterized by a lack of coordination or coherence in thought processes. Examples include:
- Loosening of associations (difficulty connecting thoughts)
- Lack of goal-directed behavior
- Impaired cognitive functioning
The Power of Understanding: Empathy and Awareness
By understanding the different categories of schizophrenia symptoms, we can work towards reducing stigma and promoting empathy for those affected. It’s crucial to recognize that individuals with schizophrenia are not defined by their condition, but rather by their unique experiences, strengths, and resilience.
In conclusion, the categorization of schizophrenia symptoms into Positive, Negative, and Disorganized categories provides a valuable framework for understanding this complex condition. By acknowledging the complexities of schizophrenia, we can work towards creating a more supportive and inclusive environment for those affected. Let’s continue to raise awareness and promote empathy – together, we can make a difference.
Other Articles You Might Find Interesting:
- Average Core Body Temperature: Discover what your body temperature says about your health! Did you know that the average core body temperature is around 98.6°F (37°C)? Learn more about its significance and how it affects your daily life.
- Red Bumps on Head of Penis: Don’t ignore those pesky bumps! Find out what’s causing them and get expert advice on how to treat them. Is it a sign of something more serious?
- Which of the Following is Not a Function of the Liver: Test your knowledge about this vital organ! What do you think is NOT a function of the liver? Learn the surprising answer and get insights on how it affects your overall health.